Modern agriculture faces unprecedented challenges. Rising global temperatures, unpredictable weather patterns, and the need to feed a growing population demand innovative solutions. Plant phenotyping methods have emerged as critical tools that enable researchers to understand how plants respond to environmental conditions, ultimately accelerating the development of resilient crop varieties. These sophisticated techniques measure plant traits ranging from growth patterns to physiological responses, providing data that drives breakthroughs in plant breeding and agricultural productivity.
Understanding Plant Phenotyping
Plant phenotyping refers to the comprehensive assessment of plant characteristics, including morphology, physiology, and performance under various conditions. Traditional methods relied heavily on manual measurements and visual assessments, which proved time-consuming and prone to subjective interpretation. Contemporary phenotyping has evolved dramatically through integration of digital sensors, automated platforms, and advanced data analytics.
The phenotype represents the observable expression of genetic traits as they interact with environmental factors. Accurate phenotyping becomes essential when researchers seek to identify genetic markers associated with desirable traits such as drought tolerance, disease resistance, or enhanced yield potential. Without precise phenotypic data, even the most sophisticated genomic information remains difficult to translate into practical agricultural improvements.
How Do Imaging-Based Methods Capture Plant Traits?
Imaging technologies form the backbone of many modern phenotyping approaches. RGB cameras capture visible light to analyze plant structure, measuring parameters like leaf area, plant height, and canopy architecture. These systems process thousands of images rapidly, extracting quantitative data that would require weeks of manual measurement.
Multispectral and hyperspectral imaging extends beyond visible wavelengths, capturing information across the electromagnetic spectrum. This enables detection of plant stress responses before visible symptoms appear, allowing early intervention. Thermal imaging measures leaf temperature, providing insights into water status and transpiration rates. Fluorescence imaging reveals chlorophyll content and photosynthetic efficiency, parameters directly linked to plant health and productivity.
Gravimetric Phenotyping Platforms
Among the various phenotyping methodologies, gravimetric platforms stand out for their ability to provide direct physiological measurements. These systems use precision weighing scales to continuously monitor changes in plant and soil weight, enabling calculation of critical parameters like transpiration rate, water uptake, and biomass accumulation. The gravimetric approach offers several distinct advantages over imaging-based methods, particularly when researchers need to understand plant-water relations.
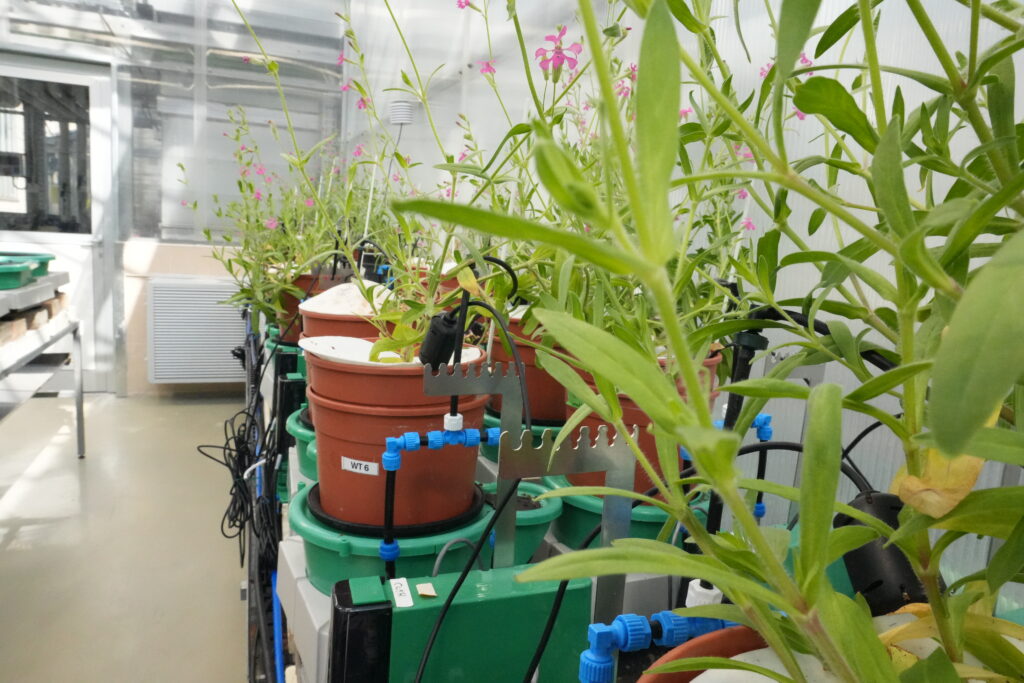
Plant-Ditech has pioneered this approach through development of the PlantArray system, a sophisticated gravimetric platform that revolutionizes how scientists study plant physiology. The system measures weight changes at intervals as frequent as three minutes, capturing dynamic responses that other methods might overlook. This temporal resolution proves invaluable when studying rapid physiological adjustments to environmental fluctuations.
Real-Time Data Collection and Analysis
The PlantArray platform continuously monitors multiple plants simultaneously while maintaining individual control over irrigation and environmental parameters for each unit. This capability eliminates confounding variables that plague traditional pot experiments where all plants receive identical treatment regardless of their individual needs. Researchers can simulate field-like conditions with personalized irrigation schedules that respond to each plant’s actual water consumption.
Weight-based measurements translate directly into physiologically meaningful parameters. Transpiration rates, water-use efficiency, and stomatal conductance calculations emerge from the continuous weight data without requiring additional sensors or invasive procedures. The system captures whole-plant responses to environmental conditions, providing a holistic view of plant performance that imaging alone cannot achieve.

What Advantages Do Automated Systems Offer?
Automation transforms phenotyping from a labor-intensive bottleneck into a streamlined, high-throughput process. Automated platforms can process hundreds of plants daily with consistent methodology, eliminating human error and subjective bias. The resulting datasets contain orders of magnitude more observations than manual approaches could generate, enabling robust statistical analysis and detection of subtle treatment effects.
Beyond efficiency gains, automated systems capture temporal dynamics that manual measurements inevitably miss. Plant responses to stress often occur rapidly, with critical physiological adjustments happening within hours. The PlantArray system exemplifies how automation enhances research capabilities while actually simplifying the experimental process. Researchers configure experiments through intuitive software interfaces, defining irrigation strategies, measurement intervals, and data collection parameters. The platform then executes the experiment autonomously.
Phenotyping Under Stress Conditions
Plant stress phenotyping represents one of the most critical applications of modern phenotyping technology. Plants encounter numerous stresses throughout their lifecycle, broadly categorized into abiotic stresses like drought, heat, and salinity, and biotic stresses including pathogens and diseases. Understanding how plants respond to these stresses proves essential for developing resilient crop varieties capable of maintaining productivity under challenging conditions.
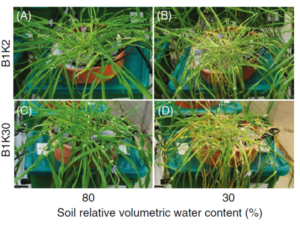
Drought stress research particularly benefits from automated phenotyping platforms. The PlantArray system excels in this application through its gravimetric approach that directly measures water consumption patterns. Researchers can impose controlled water deficit scenarios, observing how different genotypes adjust transpiration rates, close stomata, or mobilize water from soil reserves. Early detection of stress responses offers tremendous value.
Integration with Machine Learning and Advanced Analytics
The massive datasets generated by automated phenotyping platforms increasingly require machine learning tools for effective analysis. Traditional statistical approaches cannot fully exploit the rich temporal dynamics and high-dimensional nature of modern phenotyping data. Machine learning algorithms excel at identifying complex patterns and predictive relationships within these large datasets.
The PlantArray platform includes SPAC Analytics software that processes raw sensor data in real-time, calculating physiological parameters and performing statistical comparisons. Cloud-based infrastructure enables researchers to access their data remotely, monitoring experiments in progress and receiving automated alerts when predefined conditions occur. Plant-Ditech incorporates advanced analytical capabilities, supporting researchers in extracting maximum insight from their phenotyping data.
Deep learning represents a particularly powerful approach that has transformed phenotyping analysis.
How Does Plant-Ditech Support Breeding Programs?
Plant breeding programs require phenotyping tools that balance throughput with measurement quality. The PlantArray system addresses this need through scalable configurations that accommodate research objectives ranging from detailed physiological characterization to comparative screening of breeding populations. Its modular design allows facilities to start with a manageable system and expand capacity as programs grow.
For breeders focused on drought tolerance, the platform’s ability to impose precise water stress treatments while continuously monitoring plant responses proves invaluable. Researchers can identify genotypes that maintain productivity under water limitation, or those that demonstrate rapid recovery following stress relief. These functional traits often correlate more strongly with field performance than morphological characteristics alone.
The system has been successfully deployed in breeding programs where researchers used continuous transpiration data.
Why Root Phenotyping Complements Shoot Measurements
Roots represent the hidden half of plant biology, yet they fundamentally determine plant performance. Root architecture governs water and nutrient acquisition efficiency, influences drought tolerance, and affects overall plant productivity. Breeding programs traditionally focused on aboveground traits due to the difficulty of assessing root systems, but this oversight has limited genetic gains in stress tolerance and resource use efficiency.
The most comprehensive understanding emerges when researchers integrate root and shoot phenotyping. The PlantArray platform contributes valuable information about water uptake patterns that reflect root system efficiency. Variations in nighttime transpiration may indicate differences in root hydraulic conductivity. Rapid recovery following drought often correlates with extensive root systems that quickly access water from deeper soil layers once irrigation resumes.
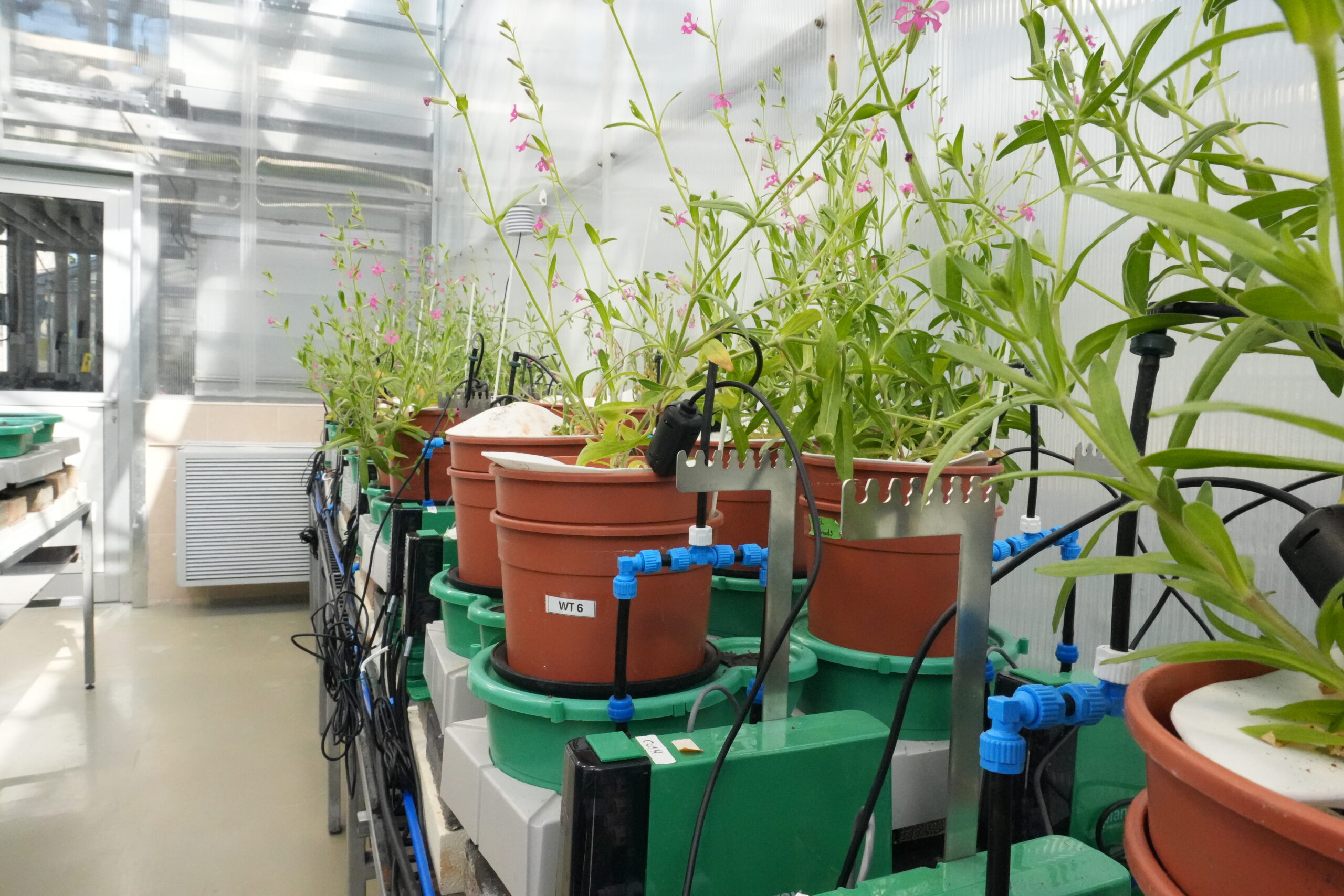

Cost-Benefit Considerations for Research Facilities
Budget constraints affect virtually every research program, making cost-effectiveness an important consideration when selecting phenotyping infrastructure. Initial capital investment in automated platforms can appear substantial compared to traditional manual methods. However, total cost analysis reveals a different picture when considering labor requirements, experimental throughput, and data quality.
Labor represents the largest ongoing expense in most research programs. Manual phenotyping requires skilled personnel to perform measurements repeatedly throughout experiments. Automated platforms like PlantArray eliminate most of this labor requirement while simultaneously increasing measurement frequency and consistency. The labor cost savings typically justify the capital investment within several years, particularly for facilities conducting multiple experiments annually. Experimental throughput amplifies the economic advantage of automation.
Global Food Security and Climate Adaptation
Global challenges of food security and climate change create urgent demand for improved crop varieties. Simultaneously, agriculture faces pressure to reduce environmental impacts by using water and fertilizer more efficiently. Meeting these demands requires crops that maintain productivity while using fewer resources and tolerating variable conditions.
Plant phenotyping addresses these challenges by accelerating development of stress-tolerant, resource-efficient varieties. Automated phenotyping compresses timelines by enabling rapid screening of large populations, continuous monitoring, ו־precise characterization of traits like water-use efficiency.
The PlantArray platform contributes to climate adaptation through its focus on water relations and stress responses. Identifying genotypes that maintain productivity under water limitation supports development of drought-resistant varieties. Plant-Ditech’s technology enables this research at high scale and precision, accelerating delivery of improved varieties to farmers.
Applications Beyond Traditional Crops
While much phenotyping research focuses on major agricultural crops, the methods prove equally valuable for horticultural species, forestry applications, and fundamental plant biology research. The PlantArray platform accommodates diverse plant sizes and pot configurations, supporting work with tree seedlings, ornamental plants, vegetables, and model organisms like Arabidopsis. This versatility enables researchers across multiple disciplines to benefit from advanced phenotyping capabilities.
Researchers studying biostimulants rely on precise phenotyping to quantify treatment effects on plant performance. The PlantArray system enables comparison of multiple biostimulant formulations under various irrigation regimes, identifying products that genuinely improve water-use efficiency or stress tolerance.
Horticultural crop improvement increasingly adopts phenotyping approaches originally developed for field crops. These diverse applications demonstrate the broad utility of modern phenotyping infrastructure.
Data Management and Standardization
Modern phenotyping generates massive datasets requiring robust data management infrastructure and standardized protocols. The PlantArray platform addresses these needs through cloud-based data storage, automated backup systems, and standardized data formats that facilitate analysis and sharing. Proper data management ensures that valuable experimental results remain accessible for years, supporting meta-analysis and replication studies that strengthen scientific conclusions.
Plant-Ditech actively participates in these collaborative efforts, contributing to development of standards that benefit the entire research community and ensure data comparability.
Data sharing among research institutions amplifies the value of individual experiments by enabling larger-scale analyses. The PlantArray platform’s standardized outputs facilitate this collaborative science, supporting researchers in addressing questions that no single institution could answer alone.
Control
PlantArray | Manual Sensors | Lysimeters | Robotic Imaging | |
Automatic Irrigation | Yes | No | Yes | Yes |
Preventing leaks | Yes | No | No | No |
Simultaneous treatments | Yes | No | No | No |
Randomization | Yes | No | No | No |
Multi treatments | Yes | No | No | No |
Dynamic feedback | Broad | No | Limited | Limited |
Measure
PlantArray | Manual sensors | Lysimeters | Imaging | |
Temporal resolution | High | Low | High | Low |
Spatial resolution | High | Low | High | Low |
Whole-plant | High | Low | High | Mid |
Functional traits precision & Yield correlation | High Whole plant | High leaf/stem | Mid Whole plant | Mid Whole plant |
Environment | Broad | Specific | Limited | Limited |
Signal to noise ratio | High | Low | Low | Low |
Manpower | Low | High | Low | Mid |
Analysis
| PlantArray | Manual sensors | Lysimeters (Data-logger) | Imaging | |
| Direct quantification | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| Real-time statistical analysis | Yes | No | No | No |
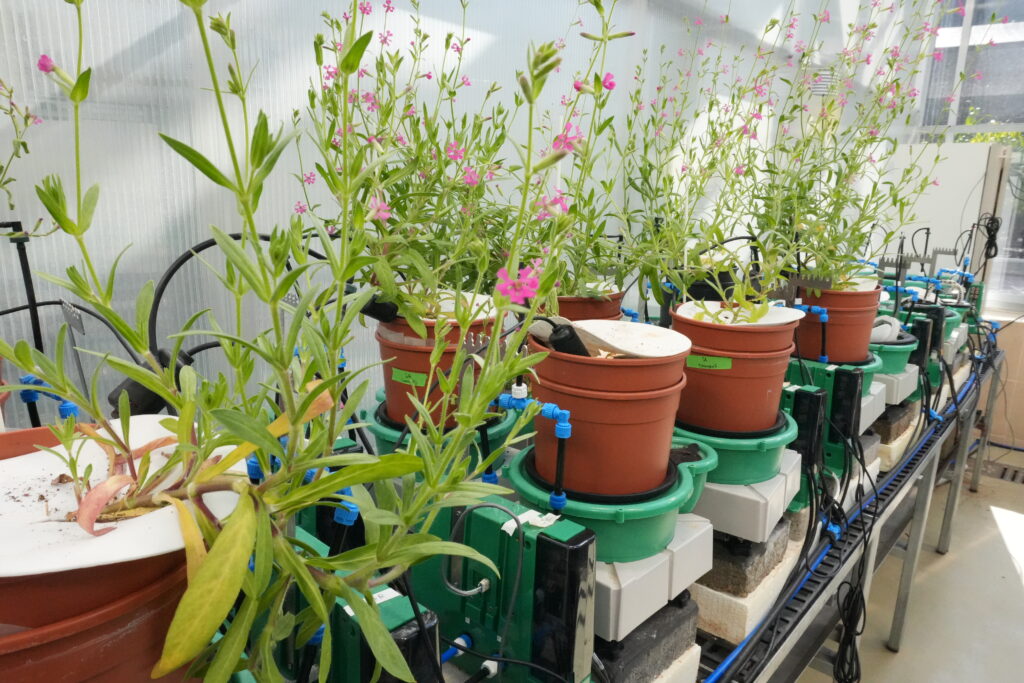

Frequently Asked Questions:
What types of plants can be studied using gravimetric phenotyping platforms?
Gravimetric platforms accommodate a wide range of plant species and sizes. The PlantArray system works effectively with agronomic crops like wheat, barley, and maize, horticultural species including vegetables and ornamentals, model organisms such as Arabidopsis, and even tree seedlings. The key requirement is that plants can be grown in pots or containers that fit the platform’s weighing units. Different pot sizes and configurations allow researchers to optimize conditions for their specific study species.
How does automated phenotyping compare in cost to traditional manual methods?
While automated phenotyping platforms require initial capital investment, they dramatically reduce labor costs over time and enable experiments at scales impossible with manual methods. A single researcher using traditional approaches might carefully phenotype 50-100 plants in a season. Automated systems can monitor thousands of plants simultaneously with minimal labor input. The per-plant cost of phenotyping typically decreases substantially when considering the volume of high-quality data generated. Additionally, automated systems work continuously, collecting nighttime and weekend data that manual approaches would miss entirely.
Can gravimetric data integrate with genomic information?
Integration of phenotypic and genomic data represents a primary objective of modern plant breeding programs. The PlantArray system generates quantitative physiological data that pairs effectively with genotyping results in genome-wide association studies and quantitative trait locus mapping. Researchers can identify genetic regions controlling traits like water-use efficiency or transpiration response to vapor pressure deficit, then use this information to develop molecular markers for breeding selection. The platform’s data export capabilities facilitate integration with standard bioinformatics pipelines.
What support does Plant-Ditech provide to new users?
Plant-Ditech offers comprehensive support throughout the platform lifecycle. Installation includes on-site training where company representatives work directly with research teams to ensure proper system setup and operation. Ongoing technical support addresses questions about system operation, experimental design, and data interpretation. The company also provides documentation, webinars, and access to a user community where researchers share experiences and methodologies. This support structure helps new users quickly achieve productive research with their phenotyping platform.
How does the PlantArray system handle diverse irrigation requirements?
Each weighing unit in the PlantArray platform includes independent irrigation control through electronically actuated valves. Researchers program irrigation strategies for individual plants or plant groups, enabling studies that compare different water regimes within a single experiment. The system can deliver precise irrigation volumes at scheduled times, or implement feedback-based irrigation that responds to actual plant water consumption. This flexibility proves essential for drought studies, irrigation optimization research, and experiments examining genotype-by-environment interactions where water availability varies.
How does gravimetric phenotyping compare with imaging-based approaches?
Gravimetric and imaging-based methods complement rather than compete with each other. Gravimetric platforms like PlantArray excel at measuring physiological parameters directly related to water relations, providing highly accurate quantification of transpiration, water uptake, and biomass accumulation. Imaging approaches capture structural information like leaf area, plant architecture, and canopy development. The most comprehensive understanding often emerges from combining both approaches. Many research facilities integrate gravimetric platforms with imaging systems, leveraging the strengths of each technology to address different aspects of plant performance.
What role does Plant-Ditech play in advancing sustainable agriculture?
Developing climate-resilient crops with improved water-use efficiency represents one of agriculture’s most pressing challenges. The PlantArray platform accelerates this work by enabling rapid identification of genotypes that maintain productivity under stress conditions. By shortening breeding cycles and improving selection accuracy, the technology helps deliver improved varieties to farmers faster. Additionally, research conducted using the platform informs irrigation management practices that optimize water use in agricultural production. Plant-Ditech’s contribution to sustainable agriculture extends through both the improved varieties and enhanced agronomic practices that phenotyping research enables.
How long does it take to see return on investment from a phenotyping platform?
Most research facilities observe positive returns within three to five years when considering total cost of ownership. Labor savings accumulate steadily as automated systems eliminate repetitive manual measurements that consume researcher time. Increased experimental throughput enables more studies per year with the same personnel, accelerating publication output and grant competitiveness. The exact timeline depends on facility utilization rates, but active phenotyping programs typically justify their investment through combination of direct cost savings and indirect benefits like enhanced research productivity and breeding program acceleration.
Can the PlantArray system be customized for specific research requirements?
The PlantArray platform offers extensive customization options to match diverse research needs and facility constraints. Researchers can configure system size from small units accommodating dozens of plants to large installations monitoring hundreds simultaneously. Pot sizes, sensor configurations, and irrigation strategies adapt to specific crop species and experimental objectives. Plant-Ditech works closely with researchers during planning stages to design optimal configurations for their particular applications, whether studying small model organisms or large crop plants requiring substantial growing volumes.
Why Choose Plant-Ditech for Your Research Needs?
Selecting a phenotyping platform is a major decision that shapes long-term research capabilities. Plant-Ditech stands out for its scientific foundation, established by Hebrew University professors who are global experts in plant physiology and soil-water science. Its platform was created by researchers who understand real phenotyping challenges. Strong technical support and ongoing collaboration further distinguish Plant-Ditech, as the company works closely with institutions worldwide and contributes expertise beyond equipment delivery. The platform’s proven track record across diverse research applications provides confidence in its versatility and reliability. This demonstrated performance across varied research contexts suggests the system will effectively support new applications as research priorities evolve. Discover how Plant-Ditech can enhance your research and support future breakthroughs by engaging with them today.