Plant genomics, the study of the complete genetic makeup of plants, is a transformative field in modern biology and agriculture. By analyzing plant genomes, researchers can uncover the genetic basis of traits like growth, stress resistance, and productivity. This knowledge drives advancements in crop breeding, genetic engineering, and sustainable agriculture. However, understanding how these genetic traits translate into physical characteristics and performance under real-world conditions requires powerful tools that link genomics to plant physiology.
The PlantArray system, a cutting-edge phenotyping platform, bridges this gap by enabling researchers to study the relationship between genetic information and plant performance under controlled conditions. This article explores plant genomics, its applications, and the ways in which the PlantArray system enhances genomic research by providing precise screening of plants’ physiological behavior to validate and apply genomic insights.

What is Plant Genomics?
Plant genomics encompasses the comprehensive study of plant genomes at a molecular level, integrating genome sequencing, functional analysis, and comparative studies across species. This discipline has evolved dramatically since the completion of the first plant genome sequence, Arabidopsis thaliana, in 2000. Recent technological advances have enabled the generation of high-quality reference genome sequences for nearly all major crop species, revolutionizing our understanding of plant biology.
The field integrates multiple layers of genomic information to decode how plants function, adapt, and respond to environmental challenges. Modern plant genomics combines cutting-edge sequencing technologies with sophisticated bioinformatics tools to unlock the secrets encoded in plant DNA, ultimately enabling researchers to develop crops better suited to feeding a growing global population under changing climate conditions.
What is the Foundation of Plant Genomics?
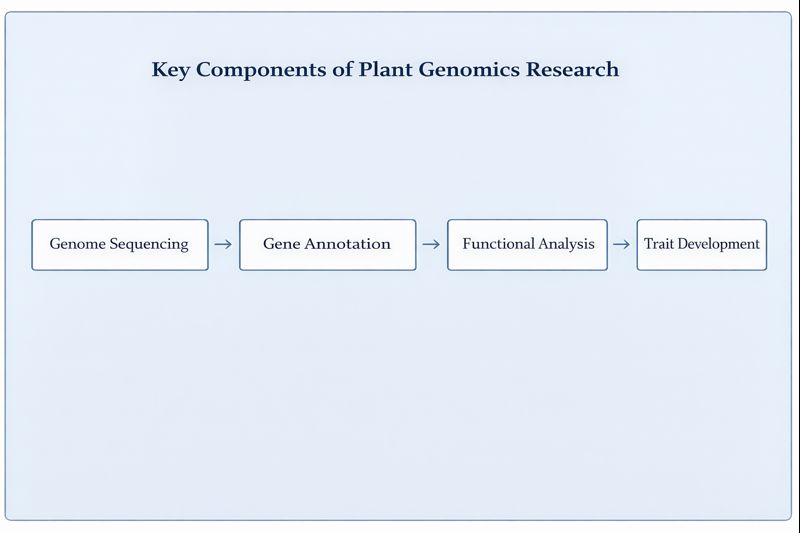
The foundation of plant genomics rests on mapping, sequencing, and analyzing the entire DNA of plants, taking earlier genetic studies to an unprecedented molecular level. This discipline builds on decades of classical genetics while leveraging modern technologies to provide genome-scale insights. Key components of plant genomics include genome sequencing, which determines the exact sequence of DNA nucleotides (A, T, C, and G) in a plant’s genome. According to recent research, the increasing availability of high-quality reference genome sequences alongside multi-omics platforms and gene-editing technologies is enabling unprecedented insights into gene functions underlying critical phenotypic traits.
Gene annotation identifies genes and their functions within the genome, while comparative genomics compares plant genomes to identify similarities and differences between species. Functional genomics explores how specific genes contribute to plant traits. The National Science Foundation’s Plant Genome Research Program supports genome-scale research addressing challenging questions of biological, societal, and economic importance, emphasizing the development of innovative tools and resources that empower the plant research community.
The goal of plant genomics is to understand the genetic basis of phenotypes, observable characteristics like plant height, drought tolerance, or seed size. However, translating genomic data into actionable insights requires linking it to measurable physiological traits, a challenge that the PlantArray system is designed to address with the help of the SPAC system.
Modern Sequencing Technologies
Contemporary sequencing platforms have dramatically reduced costs and increased throughput. The cost of DNA sequencing has plummeted from $0.52 per megabase in 2010 to approximately $0.010 in 2019, while genome sequencing costs have decreased from over $46,000 to under $1,000 for human-sized genomes. These technological advances have made large-scale plant genomics projects feasible, enabling comprehensive genome-wide association studies and population-level analyses that were previously impossible.
Bioinformatics Integration
The massive datasets generated by modern genomics research require sophisticated computational tools. Machine learning and artificial intelligence approaches are increasingly employed to extract meaningful biological insights from complex genomic data, identify gene regulatory networks, and predict phenotypes from genetic information.
Applications of Plant Genomics
Crop Improvement
Plant genomics has revolutionized crop breeding by enabling researchers to identify genes associated with desirable traits. Marker-assisted selection (MAS) and genome editing technologies like CRISPR/Cas9 allow breeders to develop crops with enhanced characteristics, such as drought resistance, improved nutrient uptake, and higher yield potential. The CRISPR/Cas9 system has been applied successfully to achieve tolerance against multiple abiotic stresses including drought, salinity, and temperature extremes in major crops.
The PlantArray system can help validate these genomic advances. By monitoring plant-water relations, transpiration, and biomass accumulation, PlantArray provides the analytics needed to confirm that plants with specific genetic modifications perform as expected under real-world stress conditions.
Research Insight: Studies show that CRISPR technology has successfully introduced important agricultural traits including heat, cold, and herbicide tolerance, as well as viral, bacterial, and fungal resistance into economically important crops such as rice, wheat, maize, tomato, and potato.
Stress Tolerance Research
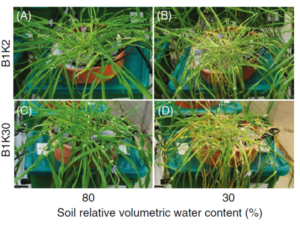
Understanding how plants respond to environmental stress is a major focus of plant genomics. Genes involved in stress tolerance, such as those controlling water-use efficiency or salinity tolerance, can be identified through genomic studies. Research demonstrates that drought tolerance is a complex quantitative trait regulated by multiple genes, representing one of the most challenging characteristics to study and classify in plant breeding.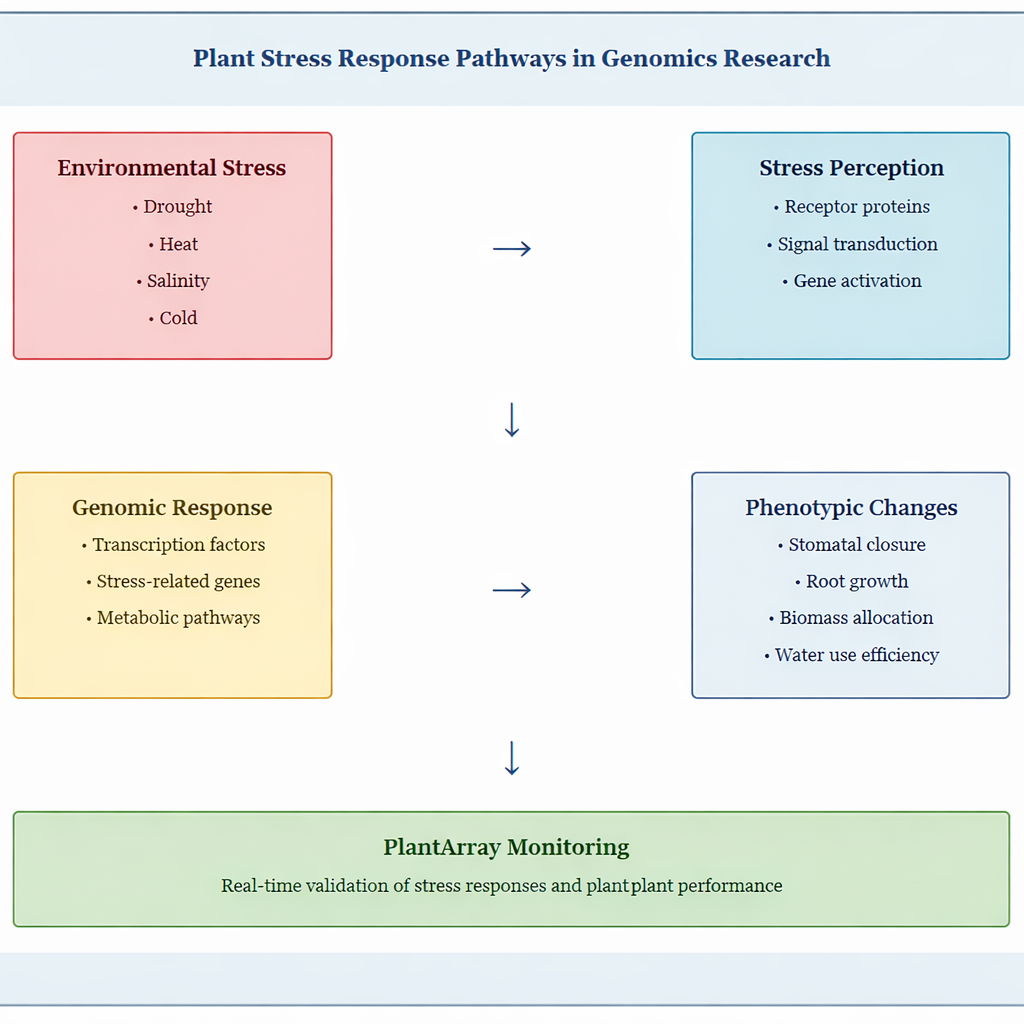
The PlantArray system enables researchers to test these genetic findings by simulating stress conditions and monitoring plant responses. Plants engineered for drought tolerance can be evaluated for their ability to maintain biomass and transpiration rates under water-limited conditions. For instance, CRISPR-edited tomato lines with modified NPR1 genes showed altered drought tolerance through changes in stomatal aperture, malondialdehyde content, and antioxidant enzyme activity.
Disease Resistance
Plant genomics has identified genes that confer resistance to diseases caused by pathogens such as fungi, bacteria, and viruses. Breeders can use this knowledge to develop disease-resistant crops, reducing reliance on chemical pesticides. PlantArray enhances this research by providing precise data on how each plant performs and comparing it to all other plants in the array.
How Does PlantArray Bridge Genomics and Phenotyping?
PlantArray serves as a critical bridge between genetic information and observable plant performance, addressing what researchers call the “phenotyping bottleneck.” Recent studies emphasize that while high-throughput DNA sequencing approaches for generating genomics data have advanced rapidly, the capacity to generate high-quality phenotypic data lags far behind. Traditional phenotyping methods rely on manual measurements that are laborious, inaccurate, and time-consuming.
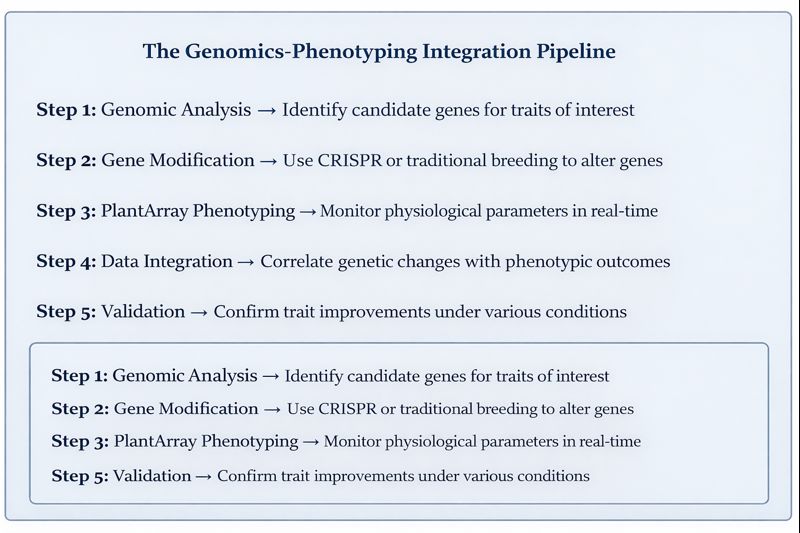
Genotype-to-Phenotype Studies
Genomics identifies genes of interest, but a phenotypic tool is needed to study how those genes influence plants under specific conditions. PlantArray’s ability to monitor multiple growth parameters, such as transpiration, biomass, and root function, provides a comprehensive phenotype profile. High-throughput phenotyping platforms like PlantArray can collect massive amounts of phenotypic data from hundreds of plants daily with a high degree of automation, enabling researchers to achieve genomics-assisted breeding through quantitative trait loci mapping and genome-wide association studies.
Environmental Interactions
PlantArray helps researchers understand how genetic traits interact with environmental factors. A gene for drought tolerance may not perform equally well in different soil types or humidity levels. By simulating diverse conditions, PlantArray tests the robustness and adaptability of genetic traits across variable environments.
High-Throughput Screening
In genomic studies, researchers often need to evaluate hundreds or thousands of genotypes. PlantArray supports high-throughput phenotyping, enabling the simultaneous monitoring of multiple plants under identical conditions. This efficiency is vital for large-scale genomic projects where statistical power and replication are essential for drawing valid conclusions.
What Is the Role of PlantArray in Functional Genomics?
Functional genomics aims to uncover the roles of specific genes in plant development, productivity, and adaptation. The PlantArray accelerates this research by providing real-time, continuous monitoring of physiological parameters that reflect gene function.
A gene identified as promoting drought tolerance can be studied using PlantArray by monitoring water-use efficiency, biomass accumulation, and transpiration rates in plants with and without the gene. Genes influencing nutrient uptake can be evaluated by analyzing function and growth under nutrient-limited conditions. PlantArray’s ability to collect real-time data on these parameters ensures that functional genomics studies are both accurate and actionable.
Case Study: Recent research on potato plants demonstrated that CRISPR/Cas9 editing of the StCBP80 gene resulted in reduced transpiration rates and improved leaf area index under water-restricted conditions, with lower yield penalties under drought stress. The study reinforces the conserved role of CBP80 in plant drought responses and demonstrates the potential of genome editing for improving stress tolerance in crops.
What Is the Role of Plant Genomics in Sustainable Agriculture?
The integration of plant genomics with phenotyping systems like PlantArray is key to achieving sustainability in agriculture. Genomic insights can lead to crops that require fewer inputs, such as water, fertilizer, and pesticides. However, these genetic improvements must be validated and optimized to ensure their success in diverse environments.
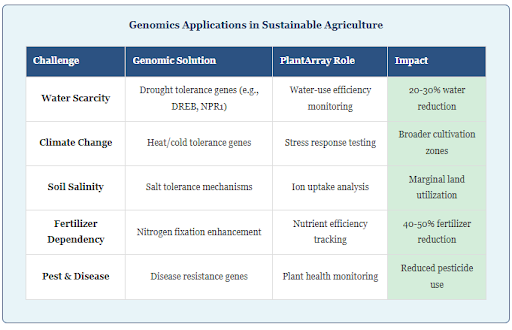
Water-Use Efficiency
Drought is one of the most pressing challenges in agriculture. Plant genomics helps identify genes that improve water-use efficiency. The PlantArray allows researchers to measure how plants balance water uptake and transpiration, ensuring that genomic modifications translate into tangible benefits. Research shows that engineering drought and salinity tolerance through CRISPR-mediated genome editing, combined with modern breeding approaches, is ideal for developing stress-resilient crops.
Climate-Resilient Crops
Climate change introduces unpredictable stressors, such as heatwaves and shifting rainfall patterns. PlantArray’s ability to conduct tests under these conditions helps researchers evaluate climate-resilient genotypes developed through genomic techniques. The platform enables assessment of how modified plants perform under scenarios that simulate future climate conditions.
Reduced Resource Dependency
Genomics can lead to crops with traits like enhanced nitrogen fixation or salinity tolerance, reducing the need for fertilizers and allowing agriculture to expand into marginal lands. PlantArray ensures that these genomic traits are optimized for real-world application by providing detailed physiological data across different growing conditions.
How Do Researchers Overcome Challenges in Plant Genomics?
Plant genomics faces several challenges, including the complexity of linking genes to phenotypes and the variability of environmental factors. The PlantArray system addresses these challenges through multiple mechanisms.
Providing Precise Data
PlantArray measures key physiological traits with high accuracy, reducing noise and improving the reliability of genotype-to-phenotype studies. The continuous monitoring capabilities ensure that transient responses and developmental changes are captured, providing a more complete picture than snapshot measurements.
Enabling Controlled Experiments
By simulating specific environmental conditions and measuring continuously, PlantArray helps isolate the effects of individual genes, making it easier to determine their function. Researchers can systematically vary environmental parameters while maintaining precise control over experimental conditions.
Facilitating Scalable Research
PlantArray’s high-throughput capabilities ensure that even large genomic studies can be conducted efficiently. The system can handle hundreds of plants simultaneously, providing the statistical power needed for genome-wide association studies and allowing researchers to screen diverse germplasm collections.
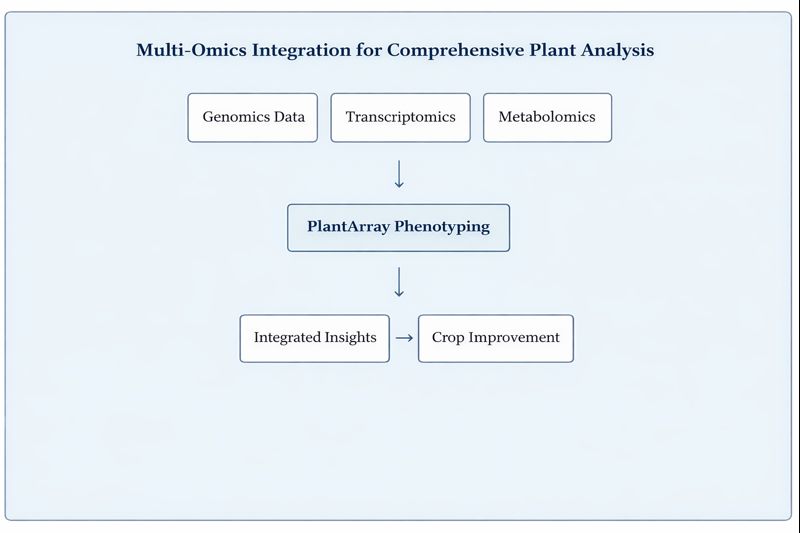
What Are the Future Directions in Plant Genomics?
The field of plant genomics continues to evolve rapidly, with several emerging trends shaping future research directions. Pan-genomics approaches that capture genetic diversity across entire species rather than relying on single reference genomes are becoming increasingly important. These approaches reveal the full spectrum of genetic variation available for crop improvement.
Synthetic biology techniques are enabling researchers to design and construct entirely new genetic pathways in plants, potentially introducing novel traits that don’t exist in nature. Multi-omics integration, combining genomics with transcriptomics, proteomics, and metabolomics data, provides comprehensive views of how genes function in biological systems.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are revolutionizing how researchers analyze genomic data and predict phenotypes. Recent advances highlight that computational tools for extracting biologically meaningful insights from large-scale datasets remain a critical need, particularly for developing robust machine learning models for accurate phenotype prediction in genomic selection.
Frequently Asked Questions:
What is the difference between plant genetics and plant genomics?
Plant genetics focuses on individual genes and their inheritance patterns, while plant genomics examines the entire genome, including all genes, regulatory elements, and their interactions. Genomics provides a comprehensive, systems-level understanding of how genetic information determines plant characteristics and responses to environmental conditions.
How long does it take to sequence a plant genome?
With modern sequencing technologies, the raw sequencing of a plant genome can be completed in days to weeks, depending on genome size and complexity. However, the complete process including assembly, annotation, and validation typically takes several months to years, particularly for species with large or complex genomes.
Why is phenotyping important in plant genomics research?
Phenotyping bridges the gap between genetic information and observable plant traits. While genomics reveals what genes are present, phenotyping shows how those genes function in real-world conditions. High-throughput phenotyping platforms like PlantArray enable researchers to connect genetic variations with actual plant performance, validating genomic discoveries and identifying promising candidates for crop improvement.
Can CRISPR technology be used safely in crop development?
CRISPR genome editing is considered safer than traditional genetic modification because it can make precise changes to a plant’s own DNA without introducing foreign genes. Many countries have developed regulatory frameworks that distinguish genome-edited crops from traditional GMOs. The technology enables targeted improvements while maintaining crop genetic backgrounds, and in some jurisdictions, genome-edited plants without foreign DNA are regulated similarly to conventionally bred varieties.
How does PlantArray help validate genomic discoveries?
PlantArray provides continuous, automated monitoring of multiple physiological parameters including transpiration, water use, biomass accumulation, and stress responses. This enables researchers to observe exactly how genetic modifications affect plant function under controlled and variable conditions. The platform’s high-throughput capabilities allow simultaneous testing of numerous genotypes, providing the statistical power needed to confirm that genomic modifications deliver the intended improvements in plant performance.
What crops have benefited most from plant genomics research?
Major crops including rice, wheat, maize, soybean, tomato, and potato have seen significant improvements through genomics research. Rice, as the first crop with a sequenced genome, has particularly benefited from genomic approaches. CRISPR technology has been successfully applied to introduce traits such as drought tolerance, disease resistance, and improved nutritional content across multiple economically important crop species.
What is the role of artificial intelligence in plant genomics?
Artificial intelligence and machine learning analyze vast genomic datasets to identify patterns, predict gene functions, and forecast phenotypes. AI algorithms can process multi-omics data to reveal complex relationships between genes and traits, accelerate gene discovery, optimize breeding strategies, and even predict how plants will perform under future climate scenarios. These computational approaches are essential for extracting actionable insights from the massive datasets generated by modern genomics research.
How does plant genomics contribute to food security?
Plant genomics accelerates the development of crop varieties that produce higher yields, resist diseases and pests, tolerate environmental stresses like drought and heat, and require fewer chemical inputs. By understanding the genetic basis of these traits, researchers can develop crops adapted to changing climate conditions and marginal agricultural lands, helping ensure stable food production for a growing global population expected to reach 10 billion by 2050.
Are You Ready to Advance Your Plant Genomics Research?
The integration of plant genomics and high-throughput phenotyping represents the future of crop improvement. The PlantArray system provides the critical link between genetic potential and real-world plant performance, enabling researchers to validate genomic discoveries and accelerate the development of improved crop varieties.
Whether you’re working on drought tolerance, disease resistance, or yield optimization, PlantArray offers the precision, throughput, and reliability needed to translate genomic insights into agricultural innovation. Discover how PlantArray can transform your research program and help you develop the climate-resilient crops the world needs.
Contact us today to learn how PlantArray can accelerate your plant genomics research and help bring your discoveries from the laboratory to the field.
References and Bibliography
- Xie, L., Gong, X., Yang, K., Huang, Y., Zhang, S., Shen, L., et al. (2024). Technology-enabled great leap in deciphering plant genomes. Nature Plants, 10, 551–566. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41477-024-01655-5
- Farooq, M.A., Gao, S., Hassan, M.A., Huang, Z., Rasheed, A., Hearne, S., et al. (2024). Artificial intelligence in plant breeding. Frontiers in Plant Science. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC12095160/
- National Science Foundation. (2024). Plant Genome Research Program (PGRP). NSF Funding Opportunities. https://www.nsf.gov/funding/opportunities/pgrp-plant-genome-research-program
- Osakabe, Y., & Osakabe, K. (2022). CRISPR–Cas9-based genetic engineering for crop improvement under drought stress. Plant Molecular Biology. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8808358/
- Razzaq, A., Saleem, F., Kanwal, M., Mustafa, G., Yousaf, S., Imran Arshad, H.M., et al. (2020). Engineering crops of the future: CRISPR approaches to develop climate-resilient and disease-resistant plants. Genome Biology, 21, 289. https://genomebiology.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13059-020-02204-y
- Zafar, S.A., Zaidi, S.S., Gaba, Y., Singla-Pareek, S.L., Dhankher, O.P., Li, X., et al. (2020). Engineering drought tolerance in plants through CRISPR/Cas genome editing. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7438458/
- Li, R., Zhang, L., Wang, L., Chen, Q., Zhao, S., et al. (2019). Reduction of tomato-plant chilling tolerance by CRISPR–Cas9-mediated SlCBF1 mutagenesis. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/plant-science/articles/10.3389/fpls.2025.1598947/full
- Sandhu, K.S., Lozada, D.N., Zhang, Z., Pumphrey, M.O., & Carter, A.H. (2022). A Comprehensive Review of High Throughput Phenotyping and Machine Learning for Plant Stress Phenotyping. Phenomics. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9590503/
- Xiao, Q., Bai, X., Zhang, C., & He, Y. (2021). Advanced high-throughput plant phenotyping techniques for genome-wide association studies: A review. Journal of Advanced Research, 35, 215-230. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8721248/
- Guo, W., Carroll, M.E., Singh, A., Swetnam, T.L., Merchant, N., Sarkar, S., et al. (2020). High-Throughput Plant Phenotyping Platform (HT3P) as a Novel Tool for Estimating Agronomic Traits From the Lab to the Field. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 8, 623705. https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/bioengineering-and-biotechnology/articles/10.3389/fbioe.2020.623705/full
- Jiang, Y., Li, C., Takeshima, R., Shu, Q., et al. (2022). Engineering drought and salinity tolerance traits in crops through CRISPR-mediated genome editing. Plant Communications. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2590346222002498
- National Human Genome Research Institute. (2019). DNA Sequencing Costs: Data from the NHGRI Genome Sequencing Program (GSP). National Institutes of Health.