Plant AI refers to artificial intelligence systems designed to monitor, analyze, and optimize plant health and growth through advanced machine learning algorithms. These systems process data from sensors, cameras, and environmental monitors to provide real-time insights that help growers make better decisions.
What makes Plant AI different from traditional monitoring? Speed and scale. A single AI system can analyze thousands of plants simultaneously, identifying patterns across multiple growth cycles that would take researchers years to document manually. This capability proves particularly valuable in controlled environment agriculture where every variable counts.
Plant-Ditech’s PlantArray system demonstrates exactly this kind of precision in action.
Plant-Ditech: AI for Better Cultivation
A groundbreaking new study published in Plant, Cell & Environment presents the first validated demonstration that daily plant transpiration can be accurately predicted using machine learning models. These models were trained on environmental parameters, supported by the continuous ground truth generated by the PlantArray system. This study highlights a major leap in the field of plant phenotyping, showcasing the power of integrating precise data collection with advanced AI-driven predictions.
The Role of PlantArray in Predicting Transpiration
This new study, “Integrating Load-Cell Lysimetry and Machine Learning for Prediction of Daily Plant Transpiration” (Friedman, S., et al., 2025, Plant, Cell & Environment, DOI: 10.1111/pce.70222), presents the first validated demonstration that daily plant transpiration can be accurately predicted using machine learning models trained on environmental parameters, supported by the continuous ground truth generated by the PlantArray system.
The researchers used the PlantArray system to gather high-resolution physiological data from plants, providing a continuous, reliable ground truth. This data formed the foundation for training machine learning models that could predict transpiration rates with impressive accuracy.
In addition to producing real-time, high-resolution data, PlantArray plays a crucial role in machine learning integration by automatically tagging every measurement point. This automatic tagging ensures that the resulting datasets are well-structured and ready for analysis, making them invaluable for machine learning models. Moreover, this structured data can be seamlessly integrated with complementary sensors, including those used for image-based analyses, to further enhance predictive capabilities.
How PlantArray Enhances Machine Learning Predictions
By capturing continuous and precise physiological data, PlantArray enables the generation of accurate, ground-truth datasets that are essential for training reliable machine learning models. These models, such as the ones demonstrated in the study, are capable of predicting plant behavior, particularly transpiration, with high accuracy based on environmental conditions.
This synergy between PlantArray’s sensor data and AI-driven predictions allows researchers to make informed decisions about irrigation, water use efficiency, and stress detection, helping to optimize plant growth conditions and resource management.

The ability to predict daily transpiration before visible stress appears opens new doors for early intervention, improving crop resilience and productivity.
Beyond transpiration prediction, Plant AI offers additional capabilities that benefit modern growers.
How Does Machine Learning Integration Enhance Plant Water Management Predictions?
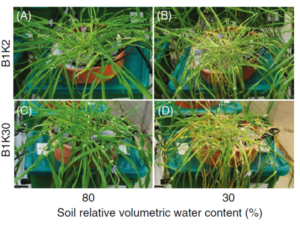
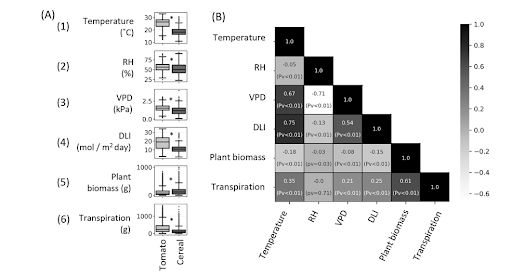
A groundbreaking study published in Plant, Cell & Environment in 2025 demonstrates the transformative potential of combining plant-ditech’s high-resolution phenotyping with machine learning algorithms. Researchers collected detailed data over seven years from hundreds of greenhouse-grown plants, leveraging the PlantArray system’s load-cell lysimetry that captures physiological measurements every three minutes. This continuous monitoring recorded daily transpiration rates alongside environmental parameters including temperature, humidity, light intensity, and atmospheric conditions.
Machine Learning Models Applied to Plant Physiological Data
The research team trained multiple machine learning models—Decision Tree, Random Forest, XGBoost, and neural networks—to predict daily plant water loss based on this rich dataset. Random Forest and XGBoost models demonstrated exceptional performance, achieving R² values of approximately 0.89 on training data and 0.82 in independent validation trials, indicating predictive accuracy nearly matching direct measurements.
Key Findings: Temperature as the Primary Factor
Among environmental variables, ambient temperature emerged as the most influential factor affecting plant transpiration rates. This insight provides actionable guidance for optimizing irrigation strategies based on real-time environmental conditions.
Practical Applications for Precision Agriculture
This integration of advanced sensor measurements with machine learning supports intelligent, precision water management in agriculture, enabling irrigation strategies based on actual plant physiological needs rather than estimated schedules. The plant-ditech system made this breakthrough possible by providing the granular, continuous data essential for training accurate predictive models.
How Does Plant AI Detect Diseases Early?
Plant AI detects diseases by analyzing visual and spectral data that reveals cellular changes before physical symptoms appear. Neural networks trained on millions of plant images can identify stress signatures invisible to the naked eye.
The process starts with image capture. High-resolution cameras or multispectral sensors photograph plants from multiple angles. Deep learning models then examine leaf color variations, texture changes, and growth patterns. Research from Bayer Crop Science demonstrates these systems can identify fungal infections 7-10 days earlier than manual inspection methods.
Early detection matters because intervention costs drop dramatically. Treating a disease affecting 5% of a crop costs far less than addressing a 40% infection rate. Cannabis cultivators using AI monitoring report 23% reduction in crop losses compared to visual inspection alone.
The technology extends beyond visible light analysis. Hyperspectral imaging captures data across electromagnetic wavelengths, revealing plant chemistry. Nitrogen deficiency, for instance, shows specific spectral signatures days before leaves yellow. Let’s examine how this monitoring translates to growth optimization.
What Environmental Factors Does Plant AI Monitor?
Plant AI systems track temperature, humidity, CO2 levels, light spectrum, soil moisture, and nutrient concentrations. These parameters directly influence photosynthesis rates and ultimately determine yield quality.
Modern AI platforms integrate data from dozens of sensors simultaneously. A study published in Scientific Reports showed that machine learning models using multi-parameter monitoring predicted harvest weight within 8% accuracy three weeks before maturity.
How accurate is temperature monitoring with AI?
AI-enhanced temperature monitoring achieves accuracy within 0.2°C by combining sensor data with predictive modeling. The systems don’t just record current temperature, they forecast micro-climate variations based on historical patterns and external weather data.
This precision prevents stress events. Cannabis plants, for example, stop optimal terpene production when temperatures exceed 28°C. AI systems trigger cooling responses before crossing that threshold, maintaining chemical profiles that affect final product quality and market value.
Can AI predict irrigation needs?
Yes, AI predicts irrigation requirements by analyzing soil moisture sensors, plant transpiration rates, and weather forecasts. These models calculate exact water volumes needed, eliminating guesswork that leads to over or under-watering.
The economic impact shows clearly. Growers using AI irrigation systems report 30-40% water savings while maintaining or improving yields. The technology pays for itself through resource conservation alone, before factoring in quality improvements.
Which Industries Benefit Most from Plant AI?
Controlled environment agriculture, pharmaceutical crop production, and specialty horticulture see the highest ROI from Plant AI implementation. These sectors share common needs: product consistency, regulatory compliance, and premium pricing that justifies technology investment.
Cannabis cultivation leads adoption rates. The industry faces strict testing requirements and operates on tight margins where a single contamination event can destroy entire harvests. AI monitoring provides the documentation and control needed to meet these standards while optimizing production efficiency.
Vertical farms represent another major adopter. These facilities control every environmental variable, making them ideal for AI optimization. Companies operating vertical farms report 15-25% yield increases after implementing comprehensive AI monitoring, according to industry data compiled by AgFunder.
How does Plant AI improve pharmaceutical crop quality?
Plant AI maintains pharmaceutical crop quality by ensuring consistent growing conditions that produce uniform chemical profiles. Regulatory bodies require batch-to-batch consistency, which traditional methods struggle to achieve.
The technology documents every parameter affecting plant chemistry. When producing medical cannabis or other pharmaceutical botanicals, this documentation proves compliance and enables quality prediction before harvest. Growers can adjust parameters mid-cycle to hit target compound ratios.
What Hardware Components Support Plant AI Systems?
Effective Plant AI requires cameras, environmental sensors, spectral analyzers, and edge computing devices. The hardware creates a data ecosystem that feeds machine learning models.
Camera systems form the foundation. RGB cameras capture visual data while multispectral and hyperspectral cameras reveal chemistry and health indicators. Mounting positions matter, some systems use fixed installations while others employ robotic platforms that move through cultivation spaces.
Environmental sensors monitor the atmosphere. CO2 sensors, temperature probes, humidity monitors, and light meters create a real-time environmental profile. Modern sensors connect wirelessly and run on low power, enabling dense sensor networks without complex wiring.
Does Plant AI work offline?
Advanced Plant AI systems run edge computing models that function without internet connectivity. This design prevents disruptions from network issues and keeps proprietary growing data secure within the facility.
Edge devices process sensor streams locally, making split-second decisions about environmental controls. Cloud connectivity serves backup and analysis functions rather than real-time operations. This architecture proved critical during a recent case where a cultivation facility maintained optimal conditions through a three-day internet outage.
ROI Metrics: What Returns Can Growers Expect?
Plant AI implementations typically show 18-month payback periods through three primary mechanisms: yield increases of 15-30%, quality improvements commanding 10-20% price premiums, and labor savings of 20-35% on monitoring tasks.
The numbers vary by operation size and crop value. A peer-reviewed analysis in the journal Agriculture tracked 12 facilities that implemented comprehensive AI monitoring. All showed positive ROI within two years, with the highest performers recouping costs in 11 months.
Labor savings often surprise operators. AI handles routine monitoring that previously required staff to walk aisles checking plants individually. Personnel shift to higher-value tasks like phenotype selection and process optimization. One facility reported redeploying three full-time monitoring positions into cultivation science roles after AI implementation.
What hidden costs should buyers consider?
Hidden costs include staff training, system integration with existing controls, and ongoing model refinement. Budget 15-20% of initial hardware costs for first-year training and optimization.
Integration challenges arise when connecting AI systems to proprietary climate controllers or fertigation equipment. Some manufacturers use closed protocols that require custom integration work. Ask vendors about compatibility before purchasing.
How Does Plant AI Handle Different Crop Types?
Plant AI adapts to different crops through transfer learning and crop-specific model training. Base models trained on general plant biology get refined with data from specific cultivars.
The adaptation process takes 2-4 growth cycles. Initial deployments use generic plant health models while collecting facility-specific data. Machine learning engineers then retrain models using this proprietary dataset, creating optimized systems that understand unique growing methodologies and genetics.
Cannabis AI models differ significantly from tomato models despite both being agricultural AI. Morphology, growth patterns, and quality indicators vary completely. Reputable vendors provide crop-specific solutions rather than one-size-fits-all platforms.
Frequently Asked Questions:
How does AI help in plant growth optimization?
AI optimizes plant growth by continuously analyzing environmental data and predicting optimal conditions for each growth stage. Machine learning models identify patterns across thousands of data points, adjusting temperature, humidity, light, and nutrients in real-time to maximize photosynthesis and biomass production. Studies show AI-optimized environments produce 15-30% higher yields compared to static environmental controls.
What is the accuracy of plant disease detection AI?
Modern plant disease detection AI achieves 92-97% accuracy rates when trained on comprehensive datasets. These systems identify diseases 7-10 days earlier than human inspection by detecting spectral signatures and subtle visual changes invisible to the naked eye. Early detection enables intervention before significant crop damage occurs.
Can small-scale growers afford Plant AI systems?
Entry-level Plant AI systems start around $5,000-$15,000 for basic monitoring of small facilities. Cloud-based solutions offer subscription models at $200-$500 monthly, making the technology accessible to operations with 1,000-5,000 square feet. ROI typically appears within 18-24 months through yield improvements and labor savings.
Does Plant AI require internet connectivity?
Advanced Plant AI systems run on edge computing, functioning without internet connectivity for real-time operations. Cloud connectivity serves data backup and long-term analysis but isn’t required for immediate environmental control and monitoring. This design maintains operations during network outages and keeps proprietary data secure.
How long does Plant AI implementation take?
Basic Plant AI installation completes in 1-2 weeks for hardware setup and initial configuration. Full optimization requires 2-4 growth cycles as the system collects facility-specific data and refines models. Most operations see measurable improvements within the first cycle, with full potential realized by cycle three.
Future Developments in Plant AI Technology
Next-generation systems will integrate genomic data with environmental monitoring. Imagine AI that adjusts growing parameters based on a plant’s genetic profile, maximizing expression of desired traits.
Platforms like PlantArray already point in this direction by providing continuous, high‑resolution measurements of water use, transpiration, biomass and plant–environment interactions, creating rich datasets that are ideal for training AI models and linking genotype to phenotype in real time.
Chemical analysis capabilities are advancing rapidly. Non-invasive sensors that measure cannabinoid or terpene content in living plants will enable real-time quality optimization. These technologies exist in laboratories today and should reach commercial facilities within two years.
Robotics integration represents another frontier. AI systems that both monitor and physically interact with plants.